Useful Mesothelioma Abbreviations and Glossary
ADRI Asbestos Diseases Research Institute
BSC best supportive care
BTS British Thoracic Society
CAM complementary or alternative medicine
CDKN cyclin-dependent kinases inhibitor gene
CEA carcinoembryonic antigen
CK cytokeratin
CT computer tomography
E(B)US endoscopic bronchial ultrasound
EMA epithelial membrane antigen
EPP extrapleural pneumonectomy
ERS European Respiratory Society
EUS endoscopic ultrasound
FISH fluorescence in situ hybridization
FNA fine needle aspiration
GP general practitioner
GLUT- glucose transporter and member of a group of membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose over a plasma membrane
Gy is a measure of the energy deposited in a medium by ionizing radiation per unit mass. Measured as joules per kilogram and represented by the equivalent SI unit, gray (Gy)
iMig International Mesothelioma Interest Group
IMRT intensity-modulated radiotherapy
LDH lactate dehydrogenase
MDT multidisciplinary team
M1 one metastatic site
MPF megakaryocyte potentiating factor
MPM malignant pleural mesothelioma
MRI magnetic resonance imaging
MVP mitomycin, vinblastine & cisplatin (chemotherapy combination)
NHMRC National Health & Medical Research Council
P/D pleurectomy/decortication
PDGFR beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta
PDT photodynamic therapy – form phototherapy using nontoxic light-sensitive compounds that are exposed selectively to light, whereupon they become toxic to targeted malignant and other diseased cells
PET positron emission tomography
PICO patient, intervention, comparison, outcome
RT-PCR reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
SMRP soluble mesothelin-related protein
SUV Standardized uptake value
TBNA trans-bronchial needle aspiration
TGV total glycolytic volume
TNM tumor, node, metastasis
TMT trimodality therapy
TTF thyroid transcription factor
TTNA trans-thoracic needle aspiration
VAT video-assisted thoracoscopy
VATS video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
WHO World Health Organization
WT Wilm’s tumor
Some useful Mesothelioma Glossary
Adenocarcinoma: cancer of glandular tissue present in surface structures of the human body.
Adjuvant chemotherapy: chemotherapy that is given in addition to the primary, main or initial treatment (surgery).
Adjuvant radiotherapy: radiotherapy that is given in addition to the primary, main or initial treatment.
Anti-cancer treatments: include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.
Asbestosis: a chronic inflammatory and fibrotic medical condition affecting the tissue of the lungs caused by the inhalation and retention of asbestos fibers.
Benign asbestos pleuritis: pleural effusion and/or thickening elicited by previous asbestos exposure.
Biomarker: An indicator of a biological state. It is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention.
Biopersistent: the persistence of a material in an organism (animals and humans).
Calretinin: a vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein involved in calcium signaling.
Carcinoembryonic antigen: a glycoprotein involved in cell adhesion that is usually not present in the blood of healthy adults.
Crocidolite: one of the types of asbestos. It is often referred to as blue asbestos.
Cuboidal: cuboid form.
Cytokeratin: proteins of keratin-containing intermediate filaments found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue.
Cytology: the study of cells.
Cytological atypia: a condition of being irregular or nonstandard.
Cytoplasmic vacuoles: small cavities in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste.
Cytoreductive surgery: surgical removal of part of a malignant tumor that cannot be completely excised, so as to enhance the effectiveness of radiation or chemotherapy. It is used only in specific malignancies, as generally partial removal of a tumor is not considered a worthwhile intervention.
Desmoplasia: the growth of fibrous or connective tissue. It is also called desmoplastic reaction to emphasize that it is secondary to an insult. Desmoplasia may occur around a tumor.
Epitheloid: an epithelioid cell is a cell that resembles epithelial cells in that it directly contacts its neighboring cells via cell surface molecules or junctions.
Erionite: a naturally occurring fibrous mineral that belongs to a group of minerals called zeolites. Some properties of erionite are similar to the properties of asbestos.
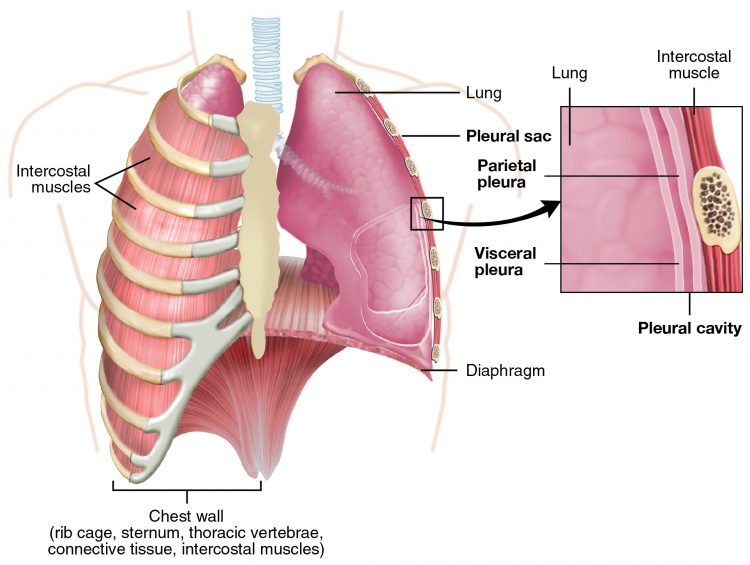
Extrapleural pneumonectomy: a surgical treatment for malignant mesothelioma. It involves the removal of a lung, a portion of the diaphragm, and the linings of the lungs and heart (parietal pleura and pericardium).
Fibrous pleuritis: an organizing inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the pleural cavity surrounding the lungs.
Histiocytoma: a tumor consisting of histiocytes.
Immunohistochemistry: the process of detecting antigens (e.g. proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies.
Leiomyosarcoma: a cancer of smooth muscle.
Lymphohistoiocytoid mesothelioma: variant of sarcomatoid mesothelioma.
Mediastinoscopy: a procedure that enables visualization of the contents of the mediastinum (central compartment of the thoracic cavity), usually for the purpose of obtaining a biopsy.
Megakaryocyte potentiating factor: a biomarker for malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Mesothelial: a tumor marker for malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Neoadjuvant: the administration of therapeutic agents before a main treatment.
Neoplasia: an abnormal mass of tissue as a result of an abnormal proliferation of cells
Pemetrexed: chemotherapy drugs used to treat malignant mesothelioma.
PICO: patient, intervention, comparison, outcome.
Pleomorphism: variability in the size and shape of cells and/or their nuclei.
Pleural effusion: excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs.
Pleural plaques: discrete fibrous or partially calcified thickened areas which can be seen on x-rays of individuals exposed to asbestos.
Pleurectomy/decortication (P/D): a form of surgery performed on patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. P/D aims to remove the lining surrounding the lung together with the tumor tissue.
Podoplanin: a human protein, the specific function of which has not been determined, but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury.
Sarcomatoid: a growth pattern resembling a malignant tumor arising from connective tissues.
Soluble mesothelin-related protein: a biomarker for malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Squamous epithelium: epithelium is characterized by its most superficial layer consisting of flat, scale-like cells called squamous epithelial cells.
Storiform: having an irregularly whorled pattern somewhat like that of a straw mat
Stromal tissue: the connective, supportive framework of tissue.
Synovial sarcoma: a rare form of cancer that usually occurs near the joints of the arm, neck, or leg.
Thoracocentesis: an invasive procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It is also known as pleural tap.
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest.
Thrombomodulin: an integral membrane protein expressed on the surface of endothelial cells which serves as a cofactor for thrombin.
Thyroid transcription factor (TTF-1): a protein that regulates the transcription of genes specific to the thyroid, lung, and diencephalon. It is also known as a thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein.
Transcription factor: sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow (or transcription) of genetic information from DNA to mRNA.
Trapped lung: unexpandable lung by constricting tumor growth and /or chronic pleural effusion.
Wilm’s tumor: A cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children. That is also known as nephroblastoma.